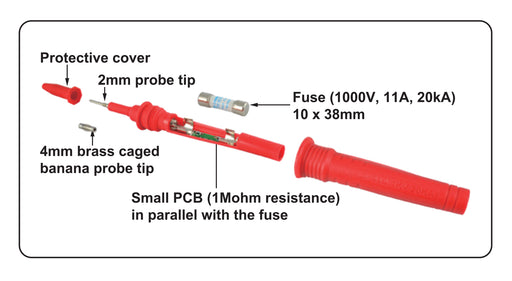
Multimeter Test Leads
Triplett offers a huge range of digital test leads for multimeter that can be used with various types and brands of digital multimeters. We offer many meter connector options and test lead sets. Our team also can assist you in finding the correct test lead for your equipment.
Test leads are an integral part of the complete measurement system. Worn out test leads can cause inaccurate readings and pose serious shock or electrocution hazard. Multimeter and Clamp leads are basically a combination of conducting materials such as wires, probes, plugs, and so on. An electrical test leads set, or a kit comprises several copper core wires, a string made of non-toxic silicone, test lead tips with nickel coating, alligator clips with a meter probe, and so on. They have soft and flexible probes which reduce the possibility of breakage. You need to choose the right model of these long meter leads made of silicone. Aside from the standard test leads, there are various test leads such as automotive, spring type, banana type, stacking, extendable, and so on. Alligator clip test leads are suited for electrical testing jobs, and are also used as jumper leads.
Filters
Categories
-
Building, Maintenance, and Environmental
- Borescopes & Inspection Cameras
- Laser Distance Meters
- Photo & Contact Tachometers
- Manometers
- CO & CO2 Meters
- F Connectors
- Combustible Gas Detector and Pen
- Humidity Indicators & Meters
- Pin & Pinless Moisture Meters
- Thermometers
- Light Meters
- Sound & Noise Level Meters
- Particle Counter
- Thermo Anemometers
- Hygro-Thermometers
- Hygrometer
- Special Kits
- Refractometer
- Coating Thickness Testers
- PH and Conductivity Meters
-
Electrical Test & Measurement
- Analog Meters -Voltmeters
- Clamp Meter
- Digital Multimeters
- Railroad Test Sets
- Voltage & Current Dataloggers
- Magnetic Field Detectors
- AC Voltage Detector
- Continuity Testers
- Test Leads
- Multimeter Case
- GFCI Receptacle Testers
- Electrical Hand Tools
- Non-Contact Voltage Detection Pens
- Circuit Breaker Tracers
- Special Kits
- Megohmmeters - Insulation Testers
- Power Supplies
- Motor & Phase Rotation Testers
-
Security, CCTV & Cabling Equipment
- Security Camera Testers
- CCTV HD LED Test Monitors
- Baluns, Ground Loop Isolators
- HDMI & IP Extenders
- All Cables
- HDMI Cables
- CAT6a Shielded Cable
- Ethernet Network Cables
- CCTV BNC Adapters
- BNC Connectors
- F Connectors
- BNC Compression Connectors
- CAT5 & CAT6 Connectors
- CCTV Coax Connectors
- Modular Connector
- Between Series Adapters
-
Original price $44.00 - Original price $44.00Original price$44.00$44.00 - $44.00Current price $44.00| /
42" Test Leads with Mini-Banana Jacks and Insulated Screw-On Alligator Clips for Triplett 310 Series - (79-153)
TriplettIn stock0 Reviews
Triplett 42" Test Leads (79-153) with mini-banana jacks and insulated screw-on alligator clips. Color-coded and designed for the Triplett 310 serie...
View full detailsOriginal price $44.00 - Original price $44.00Original price$44.00$44.00 - $44.00Current price $44.00| / -
Original price $27.00 - Original price $27.00Original price$27.00$27.00 - $27.00Current price $27.00| /
48" Universal Banana Test Lead Set: Includes Insulated Screw On Alligator Clips - (79-127)
TriplettIn stock0 Reviews
These 48" Test Leads with mini-banana jacks are for use with Triplett Model 630 Type 1, 2, and 3, 630-NA, 630-NS, 630-PL, 630-PLK, 666-R and G/P Se...
View full detailsOriginal price $27.00 - Original price $27.00Original price$27.00$27.00 - $27.00Current price $27.00| / -
Original price $32.00 - Original price $32.00Original price$32.00$32.00 - $32.00Current price $32.00| /
48" Test Leads with Insulated Screw-On Alligator Clips : Female Jack -(79-374)
TriplettIn stock0 Reviews
These 48" Test Leads with female jacks are for use with Triplett Models 60, 60-NA, 630 Type 4 and later meters. They include insulated screw-on all...
View full detailsOriginal price $32.00 - Original price $32.00Original price$32.00$32.00 - $32.00Current price $32.00| / -
Free with Any Two MultimetersOriginal price $25.00 - Original price $25.00Original price$25.00$25.00 - $25.00Current price $25.00| /
55" Universal Standard Test Leads with Insulated Push-On Alligator Clips: Fits Most Major Brand Digital Multimeters - (TL005)
TriplettIn stock0 Reviews
Universal design fits virtually all major brand digital multimeters and test instruments. They include insulated screw-on alligator clips. CATEGO...
View full detailsOriginal price $25.00 - Original price $25.00Original price$25.00$25.00 - $25.00Current price $25.00| / -
Original price $33.00 - Original price $33.00Original price$33.00$33.00 - $33.00Current price $33.00| /
Electronic 42" Test Lead Kit - (TLK008)
Triplett Test Equipment & ToolsIn stock0 Reviews
The Triplett TLK008 electronic test leads feature a universal design that fits virtually all major brand digital multimeters and test instrumen...
View full detailsOriginal price $33.00 - Original price $33.00Original price$33.00$33.00 - $33.00Current price $33.00| / -
Original price $23.00 - Original price $23.00Original price$23.00$23.00 - $23.00Current price $23.00| /
Flat Tip Blade Probes - (TL009-FLAT)
TriplettIn stockFlat Tip Blade Probes for use with modular test leads CATEGORY: TEST LEADS FAQs Q. What are universal test leads? A. Universal test leads...
View full detailsOriginal price $23.00 - Original price $23.00Original price$23.00$23.00 - $23.00Current price $23.00| / -
Original price $95.00 - Original price $95.00Original price$95.00$95.00 - $95.00Current price $95.00| /
Moduleads Premium Silicone Jacketed 24" and 60" Test Leads- (79-812)
TriplettOut of stock0 Reviews
The Triplett ModuLeads™ is a premium modular test lead kit that is designed to work all major brand digital multi-meters. This set of high quality ...
View full detailsOriginal price $95.00 - Original price $95.00Original price$95.00$95.00 - $95.00Current price $95.00| /Out of Stock -
Original price $68.00 - Original price $68.00Original price$68.00$68.00 - $68.00Current price $68.00| /
Universal 42" Test Leads with Mini Banana to Angled Bed of Nails Clips
Triplett Test Equipment & ToolsIn stockTriplett 79-695 Universal Test Leads with Mini Banana to Angled Bed of Nails Clips are a high-quality addition to your digital multimeter tool kit....
View full detailsOriginal price $68.00 - Original price $68.00Original price$68.00$68.00 - $68.00Current price $68.00| / -
Original price $18.00 - Original price $18.00Original price$18.00$18.00 - $18.00Current price $18.00| /
Male to Male Banana test leads - (TL007)
TriplettIn stock47" (1.2m) PVC test leads with straight shrouded banana plugs on one end and right-angled shrouded banana plugs on the other end.
Original price $18.00 - Original price $18.00Original price$18.00$18.00 - $18.00Current price $18.00| / -
Original price $28.00 - Original price $28.00Original price$28.00$28.00 - $28.00Current price $28.00| /
Plunger-Style Mini Hook Test Leads: Fit virtually all major brand digital multimeters and test instruments - (TL20)
TriplettIn stockThe Triplett Model TL20 Plunger-Style Mini Hook 40" PVC Test Leads with right-angle shrouded standard banana jacks fit virtually all major brand di...
View full detailsOriginal price $28.00 - Original price $28.00Original price$28.00$28.00 - $28.00Current price $28.00| / -
Original price $254.00 - Original price $254.00Original price$254.00$254.00 - $254.00Current price $254.00| /
CATIV Fused Test Leads - Fit virtually all major brand digital multimeters and test instruments - (TL15)
TriplettIn stockThe Triplett Model TL15 has a universal design and fits virtually all major brand digital multimeters and test instruments. It Provides additional ...
View full detailsOriginal price $254.00 - Original price $254.00Original price$254.00$254.00 - $254.00Current price $254.00| / -
Original price $13.00 - Original price $13.00Original price$13.00$13.00 - $13.00Current price $13.00| /
Stacking Banana Plug - (TL25)
TriplettIn stockThe Triplett Model TL25 Stacking Banana Plugs are used for creating custom banana jack test leads that can be stacked. They accept 18 awg test lead...
View full detailsOriginal price $13.00 - Original price $13.00Original price$13.00$13.00 - $13.00Current price $13.00| /
Know More About Triplett Test Leads
What Are Electrical Test Leads?
Test leads are primarily wire-like testing and measuring devices. It is used to test and measure the current in a circuit. These are simple devices which are coated and colored to indicate positive and negative with the device connector on one end. On the other end, they have a metal conductor such as an alligator clip or banana tip. Alligator clip leads are widely used. They are slightly different from test probes. Triplett offer superior quality multimeter test lead sets which offer an accurate reading. Quality and accuracy are important because incorrect readings of a meter may be the reason for a mishap. We use good quality similar metals, and hence they do not produce their own voltage when measuring current. Our multimeter lead sets are designed to identify defects in very low voltage circuits as well.
What are Multimeter Test Leads?
Multimeter test leads, sometimes referred to as test probes or probe leads, are vital tools utilized alongside multimeters to perform electrical measurements and testing. These leads comprise a set of insulated wires equipped with connectors or probes affixed to their respective ends. Here's an overview of multimeter test leads:
- Insulated Wires: The test leads are constructed using insulated wires, which facilitate electrical conductivity while ensuring protection against electrical shocks. The insulation serves as a safeguard, directing the current along the intended pathway and preventing unintended contact with live wires.
- Connector Types: Test leads are available in a range of connector types designed to accommodate different multimeter models. Common connector options include banana plugs, alligator clips, and needle probes. These connectors are specifically engineered to establish secure connections between the test leads and the input jacks of the multimeter, ensuring reliable and stable electrical contact.
- Probes: At the opposite extremity of the test leads, you'll find probes or tips designed to establish electrical contact with the circuit or component being tested. These probes are commonly crafted from metal and can feature sharp tips for puncturing wires or spring-loaded jaws for clamping onto terminals. Their purpose is to facilitate accurate and secure connections for precise measurements during electrical testing.
- Color Coding: To ensure proper identification and consistent connections during measurements, test leads are frequently color-coded. This color scheme serves to differentiate between positive and negative polarities or various functions. The most widely used color convention involves using red for positive (+) connections and black for negative (-) or common (ground) connections. This standardized color coding system aids technicians in making accurate and reliable connections, promoting consistent and error-free measurements.
- Versatile Functions: Multimeter test leads are incredibly versatile tools that empower users to perform a wide array of electrical measurements. They are capable of measuring voltage, current, resistance, continuity, capacitance, and other essential electrical parameters. The appropriate selection of probes and connectors depends on the specific measurement needs and objectives. With the right combination of probes and connectors, technicians can confidently tackle diverse electrical measurement tasks and achieve accurate and reliable results.
- Flexibility and Length: Test leads are available in various lengths, offering users the flexibility and reach required to access different areas of the circuit or equipment being tested. Longer test leads provide enhanced freedom of movement and improved accessibility, particularly in intricate or hard-to-reach systems. These extended lengths enable technicians to navigate around obstacles and maneuver comfortably, ensuring efficient and effective measurements in a wide range of testing scenarios.
- Replacement and Upgrade: Test leads are subject to wear and tear over time, especially at the probe tips. It is important to regularly inspect and replace damaged or worn-out test leads to maintain accurate measurements. Additionally, high-quality test leads with better insulation and robust construction can improve measurement accuracy and reliability.
Why Are Test Leads Important in Multimeters?
Multimeter leads are used to identify issues in analog meter as well as digital multimeters. It check the electrical components as well as the circuits. We offer a multimeter test lead kit, wherein the test leads are designed to measure circuits and components in diverse environments. They are important because they help prevent mishaps in the form of shocks, leakages, short circuits, and so on.
How to Use Multimeter Test Leads?
It’s quite easy to use test lead with a multimeter if you follow the process steps. The multimeter device display has resistance and OL outputs. There are a number of buttons of which you may need to push the continuity button. Our test leads are compatible with most multimeter devices and are useful for measuring analog as well as digital circuits. Here are the steps you can follow.
- Take the black test lead and place it in the COM jack on the multimeter device. After that, place the red test lead and place it in VΩ jack.
- Check the readings on the device and remove the test leads in the reverse order.
- Place these test leads on the opposite ends of a component being tested and ensure the circuit is deactivated.
- Separate the component under test from the other components in the circuit if required.
- The multimeter will indicate through a beep sound if the circuit path is identified. It will not produce a beep sound in case of any open ends or gaps in the circuit, which means there is an issue.
Are multimeter test leads universal?
If you're new to using a multimeter, you may be wondering if the test leads are universal. The answer is: it depends. While some multimeters come with test leads that can be used with any type of device, others may require specific test leads for certain types of devices. Being said this, most multimeter test leads are universal, meaning they can be used with any multimeter. However, there are a few exceptions. Some multimeters have special ports that can only be used with specific test leads. Also, some test leads are only compatible with certain types of multimeters. So it's always a good idea to check the compatibility of your test leads before investing in them.
What are the types of test probes of the multimeter?
Test probes are essential tools to ensure the safety of electrical workers. These wires are insulated and highly flexible, allowing them to make electrical connections between a multimeter and devices under test without exposing personnel to dangerous live conductive components.
There are four test probes of the multimeter: the red positive (+) probe, the black negative (-) probe, the common ground probe, and the test lead probe. The red positive (+) probe is used to measure positive voltage, the black negative (-) probe is used to measure negative voltage, the common ground probe is used to establish a connection to ground, and the test lead probe is used to make electrical contact with the test point.
At What Resistance Should Test Leads on a Multimeter be Discarded?
It is important to inspect the accuracy of the test leads through visual and other tests such as Ohms resistance measurement. This assures the electrical accuracy and reliability of leads. Ideally, good-quality leads have a resistance of around 0.5 ohms or less than that, and the same would be displayed on the multimeter. The multimeter would produce a beep sound for the same; however, it may produce the sound for resistance up to 15 ohms.
To check this, you need to switch on the resistance function of the multimeter and plug the test leads into the device. Do this by placing both the lead tips together. You can do this for one or a single test lead or one at a time. Do not keep it static; you need to move or shake it to check, and do a continuity check. The multimeter and test leads need to work together and offer accurate output. So, check thoroughly if you notice any changes or if the multimeter does not give a beep sound at any point in time. If that happens, you may want to replace your test leads. In fact, if your application demands continual use of test leads or they are exposed to stress environments very often, it is good to replace them once in a year or so.
Browse More Electrical Test & Measurement Collections
Multimeters & Clamp-On Meters:
| Analog Multimeters | Clamp-On Multimeters | Digital Multimeters |
| Railroad VOM Test Sets | Voltage & Current Dataloggers | Magnetic Field Testers |
| AC Voltage Detector | Continuity Testers | Multimeter Case |
Electrical Accessories:
| GFCI Receptacle Testers | AC Line Splitters | Electrical Hand Tools |
| Non-Contact Voltage Detection Pens | Circuit Breaker Tracers |
Megohm & Resistance Testers:
| Megohmmeters - Insulation Testers | Earth Ground Resistance Testers |
Live Wire Circuit Testers:
| Live Wire Tone & Probe Kit |
Specialty:
| Power Supplies | Motor & Phase Rotation Testers |